What is the Emergency Manuals Implementation Collaborative?
 The Emergency Manuals Implementation Collaborative (EMIC) fosters adoption and effective use of emergency manuals to enhance patients’ safety. Its initial focus is perioperative care, while sharing our lessons with other fields of healthcare. EMIC’s goals are to share knowledge and resources to effectively implement and use emergency manuals to manage, debrief and train for critical events. It is an interprofessional, global community of 500 developers, researchers and users of emergency manuals. (EMIC Steering Committee roster)
The Emergency Manuals Implementation Collaborative (EMIC) fosters adoption and effective use of emergency manuals to enhance patients’ safety. Its initial focus is perioperative care, while sharing our lessons with other fields of healthcare. EMIC’s goals are to share knowledge and resources to effectively implement and use emergency manuals to manage, debrief and train for critical events. It is an interprofessional, global community of 500 developers, researchers and users of emergency manuals. (EMIC Steering Committee roster)
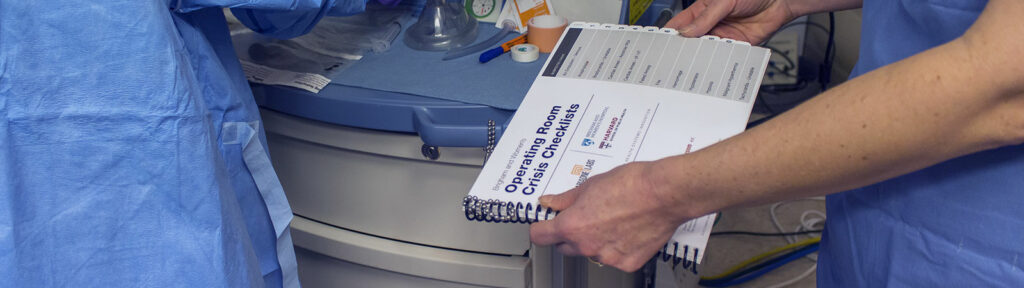
Definition of Emergency Manuals, Crisis Checklists, Cognitive Aids
These terms refer to print and/or electronic materials designed to assist clinicians in real-time delivery of accurate and thorough care during critical events. They typically have supplementary applications such as education or case review. Their content, format and use reflect decades’ of experience with emergency checklists in other industries, notably aviation. While anesthesia professionals have a special interest in these tools, they are intended to be accessible to the entire perioperative team.
Rationale
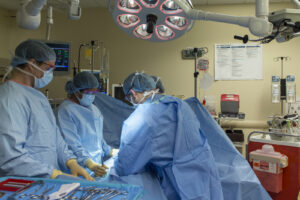 Management of critical events is a very stressful event, especially when the event is rare and thus unfamiliar to the clinician despite prior education and training. This stress degrades cognitive performance and tools to bridge the gap between “available knowledge” and optimal performance are valuable. A shared cognitive aid or checklist can provide a common understanding of key management steps for the entire perioperative team. Multiple trials of OR checklists have demonstrated improved performance in simulated critical events when checklists are used.
Management of critical events is a very stressful event, especially when the event is rare and thus unfamiliar to the clinician despite prior education and training. This stress degrades cognitive performance and tools to bridge the gap between “available knowledge” and optimal performance are valuable. A shared cognitive aid or checklist can provide a common understanding of key management steps for the entire perioperative team. Multiple trials of OR checklists have demonstrated improved performance in simulated critical events when checklists are used.
Major OR Cognitive Aids: Ariadne Labs (Harvard), Stanford, SPA
The most widely used OR emergency manuals are offered free of charge by Ariadne Labs (Harvard), Stanford University and the Society for Pediatric Anesthesia.
Links to these and many other more specialized tools and those developed outside the US are provided in the Free Tools section of the EMIC website.
Mobile Apps
The Society for Pediatric Anesthesia (SPA) free mobile app “Pedi Crisis 2.0” is available for download on iOS and Android.
Key conclusions of 2015 APSF Experts’ Workshop
In 2015, APSF convened an Experts’ Workshop focused on implementation of Emergency Manuals. Expert panelists and participants reviewed the current state and future of operating room emergency manuals. The potential value of these tools was widely recognized, and the need to develop a deeper understanding of their benefits, risks and particularly optimal implementation strategies was noted. Among the conclusions of the workshop was the observation that “a large majority of the audience felt that the APSF should take a leading role in promoting EMs.”
Emergency Manuals and APSF Strategic Priorities
For 2022, APSF has identified its top ten patient safety priorities. The use of emergency manuals is highly relevant to the top three of these priorities: culture of safety, teamwork and clinical deterioration.
What resources are available from EMIC?
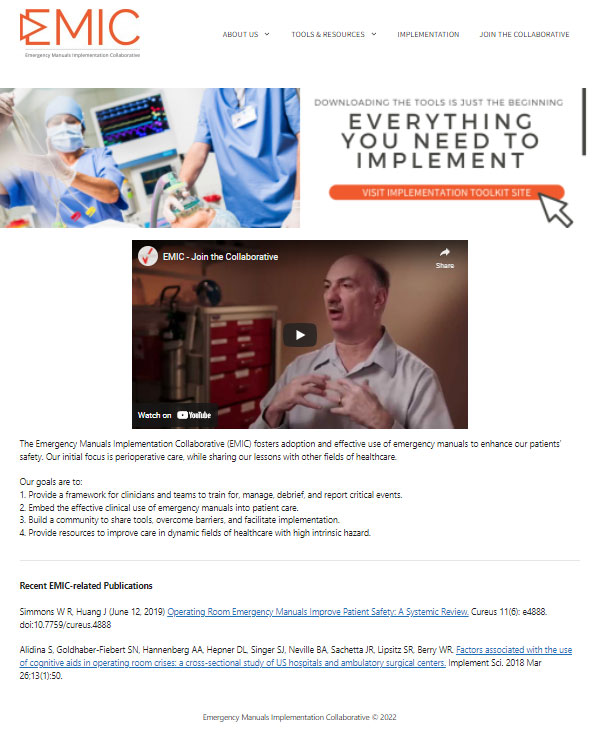 EMIC Website
EMIC Website
The EMIC website is widely used to access the major available checklists and also manuals for subspecialty practice and those originated outside the US. A regularly updated catalog of relevant literature is provided along with an archive of prior EMIC webinar programs. A video library is also available with material suitable for launching an implementation program and training clinical teams in the use of emergency manuals.
 Implementation Toolkit
Implementation Toolkit
With support from EMIC, the teams at Ariadne Labs and Stanford developed an Implementation Toolkit to guide your journey all the way from acquiring the checklists/manuals to establishing goals for its use in your organization, training your teams, and improving the care you provide to patients who experience critical events. Toolkit content is inspired by insights emerging from a two-year clinician study of checklist implementation, supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and conducted by Harvard and Stanford. Resources built into the Toolkit are many of those identified as valuable in the implementation process including training materials, presentations, and videos.